Welcome!... To Shri Sigma Hospitals.
Managing PCOS Naturally:Diet, Exercise, and Holistic Approaches
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. This condition is characterized by irregular menstrual periods, excessive levels of male hormones (androgens), and polycystic ovaries that contain numerous small cysts. PCOS can have a profound impact on a woman’s health, influencing everything from fertility and menstruation to overall physical and emotional well-being.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide a deeper understanding of PCOS by exploring its symptoms, causes, types, complications, prevention strategies, and treatment options. Armed with this knowledge, individuals can better manage their symptoms, improve their quality of life, and seek appropriate medical care.
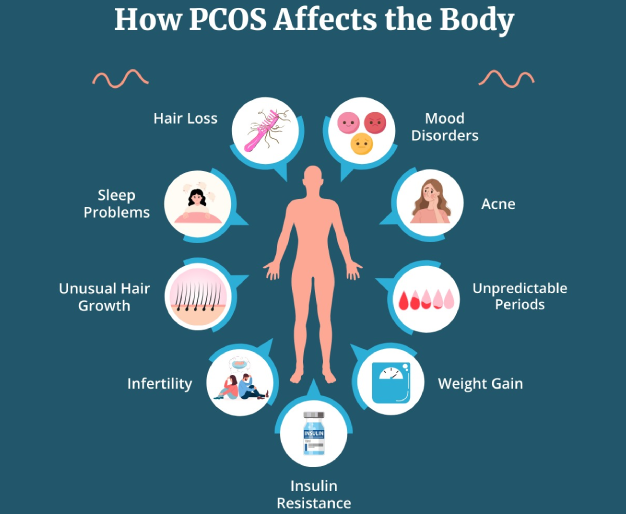
Common Symptoms of PCOS
The symptoms of PCOS can vary from mild to severe and may manifest differently in each individual. Some of the most common symptoms include:
Irregular menstrual cycles or absence of periods
Excessive hair growth (hirsutism) on the face, chest, or back
Acne or oily skin
Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
Thinning hair or hair loss from the scalp
Darkening of the skin, particularly around the neck, groin, or under the breasts
Polycystic ovaries visible on ultrasound
Causes of PCOS
While the exact cause of PCOS remains unclear, several factors are thought to contribute to its development, including:
Genetics: A family history of PCOS may increase the risk of developing the condition.
Insulin resistance: Many women with PCOS have insulin resistance, leading to elevated insulin levels that may affect ovarian function.
Hormonal imbalance: High levels of androgens (male hormones) interfere with ovulation, leading to irregular menstrual cycles.
Low-grade inflammation: Women with PCOS may have low-grade inflammation that stimulates the ovaries to produce androgens.
Types of PCOS
PCOS can present in different forms, categorized based on the symptoms and underlying causes. These include:
Insulin-resistant PCOS: The most common type, characterized by insulin resistance and high insulin levels.
Inflammatory PCOS: Linked to chronic inflammation, this type presents with elevated inflammatory markers.
Post-pill PCOS: Occurs after discontinuing birth control pills, particularly in those predisposed to PCOS.
Adrenal PCOS: Caused by an overproduction of androgens by the adrenal glands, usually due to stress or adrenal disorders.
Complications of PCOS
Without proper management, PCOS can lead to several complications, including:
Infertility or difficulty conceiving
Type 2 diabetes or prediabetes
High blood pressure and heart disease
Sleep apnea
Depression and anxiety
Endometrial cancer due to prolonged lack of ovulation
Preventive Measures for PCOS
While PCOS cannot be entirely prevented, certain lifestyle changes may help reduce the risk and manage symptoms effectively:
Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced diet and regular exercise
Monitoring blood sugar levels and managing insulin resistance
Reducing stress through mindfulness practices, yoga, or meditation
Getting regular medical check-ups and screenings for associated conditions
Treatment Options for PCOS
The treatment of PCOS often involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgery, depending on the symptoms and individual needs:
Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, healthy diet, and weight management are fundamental to managing PCOS symptoms.
Medications: Birth control pills, anti-androgens, and insulin-sensitizing agents are commonly used to regulate periods, reduce androgen levels, and improve insulin sensitivity.
Fertility treatments: For women struggling with infertility, treatments like ovulation induction or in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be recommended.
Surgery: In rare cases, laparoscopic ovarian drilling may be considered to stimulate ovulation.
Conclusion
PCOS is a complex condition that requires a multi-faceted approach to manage effectively. By understanding the symptoms, causes, types, complications, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage PCOS and improve their quality of life. Consulting with healthcare professionals, embracing healthy lifestyle habits, and seeking support from peers and support groups can be pivotal in navigating the challenges associated with PCOS.

Leave A Reply